Time, accurate time – to be more precise is very important in modern IT systems. There is no difference in Nutanix AOS. Heaving reliable time source in your network is a key to avoid unpleasant surprises such as data inconsistency. In addition, heaving consistent time across the board helps in analysis and troubleshooting.
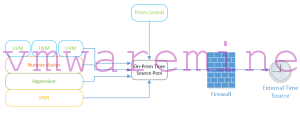
Time sync Schema
First, configure NTP server using Prism UI
Log in to one of the CVMs and run
allssh ssh root@192.168.5.1 date
to check time on AHV
nutanix@NTNX-15SM65300246-A-CVM:10.4.91.56:~$ allssh ssh root@192.168.5.1 date Executing ssh root@192.168.5.1 date on the cluster ================== 10.4.91.56 ================= FIPS mode initialized Tue Dec 15 02:46:57 PST 2015 ================== 10.4.91.57 ================= FIPS mode initialized Tue Dec 15 02:48:20 PST 2015 ================== 10.4.91.58 ================= FIPS mode initialized Tue Dec 15 02:49:04 PST 2015 nutanix@NTNX-15SM65300246-A-CVM:10.4.91.56:~$
check what is the source time server your AHV hosts are getting time from
nutanix@NTNX-15SM65300246-A-CVM:10.4.91.56:~$ allssh ssh root@192.168.5.1 ntpq -p
Executing ssh root@192.168.5.1 ntpq -p on the cluster
================== 10.4.91.56 =================
FIPS mode initialized
remote refid st t when poll reach delay offset jitter
==============================================================================
us.pool.ntp.org 16 u 90 1024 0 0.000 0.000 0.000
================== 10.4.91.57 =================
FIPS mode initialized
remote refid st t when poll reach delay offset jitter
==============================================================================
us.pool.ntp.org 16 u 26 1024 0 0.000 0.000 0.000
================== 10.4.91.58 =================
FIPS mode initialized
remote refid st t when poll reach delay offset jitter
==============================================================================
us.pool.ntp.org 16 u 625 1024 0 0.000 0.000 0.000
nutanix@NTNX-15SM65300246-A-CVM:10.4.91.56:~$
Stop ntpd daemon
nutanix@NTNX-15SM65300246-A-CVM:10.4.91.56:~$ allssh ssh root@192.168.5.1 service ntpd stop Executing ssh root@192.168.5.1 service ntpd stop on the cluster ================== 10.4.91.56 ================= FIPS mode initialized Shutting down ntpd: [ OK ] ================== 10.4.91.57 ================= FIPS mode initialized Shutting down ntpd: [ OK ] ================== 10.4.91.58 ================= FIPS mode initialized Shutting down ntpd: [ OK ] nutanix@NTNX-15SM65300246-A-CVM:10.4.91.56:~$
Update time from time servers
nutanix@NTNX-15SM65300246-A-CVM:10.4.91.56:~$ allssh ssh root@192.168.5.1 ntpdate -u us.pool.ntp.org Executing ssh root@192.168.5.1 ntpdate -u us.pool.ntp.org on the cluster ================== 10.4.91.56 ================= FIPS mode initialized 15 Dec 03:28:10 ntpdate[16907]: adjust time server 208.75.88.4 offset -0.014000 sec ================== 10.4.91.57 ================= FIPS mode initialized 15 Dec 03:28:20 ntpdate[14812]: adjust time server 208.75.88.4 offset -0.001235 sec ================== 10.4.91.58 ================= FIPS mode initialized 15 Dec 03:28:30 ntpdate[12209]: adjust time server 208.75.88.4 offset -0.019629 sec nutanix@NTNX-15SM65300246-A-CVM:10.4.91.56:~$
Start NTP demon again
allssh ssh root@192.168.5.1 service ntpd start
Now, clock on AHV is fine
nutanix@NTNX-15SM65300246-A-CVM:10.4.91.56:~$ allssh ssh root@192.168.5.1 date Executing ssh root@192.168.5.1 date on the cluster ================== 10.4.91.56 ================= FIPS mode initialized Tue Dec 15 03:30:39 PST 2015 ================== 10.4.91.57 ================= FIPS mode initialized Tue Dec 15 03:30:40 PST 2015 ================== 10.4.91.58 ================= FIPS mode initialized Tue Dec 15 03:30:41 PST 2015 nutanix@NTNX-15SM65300246-A-CVM:10.4.91.56:~$
You can check time on AOS by execute NCC checks script. NCC – Nutanix Cluster Check is set of checks used to check overall cluster health and identify other possible problems. This allows the user to be more proactive instead of reactive and fix possible issues ahead of time. This tool will not only check for Nutanix operating system (NOS) problems but also for any hypervisor related issues.
To run NCC, log in to Nutanix CVM and run command
nutanix@NTNX-15SM65300246-A-CVM:10.4.91.56:~$ ncc +---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+ | Type | Name | Impact | Short help | +---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+ | M | cassandra_tools | N/A | Plugins to help with Cassandra ring analysis | | M | config_based | N/A | All config based plugin | | M | file_utils | N/A | Utilities for manipulating files on the cluster | | M | fix_failures | N/A | Fix failures | | M | health_checks | N/A | All health checks | | M | help_opts | N/A | Show various options for ncc. | | M | insights_collectors | N/A | Plugin to start the insights collectors | | M | log_collector | N/A | Collect logs on all CVMs. | +---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+ nutanix@NTNX-15SM65300246-A-CVM:10.4.91.56:~$ ncc health_checks run_all

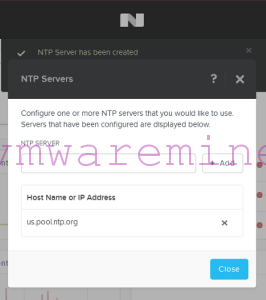

Hello, just one question,
How to update the exsiting NTPs with 2 sources?
service ntpd stop
ntpdate –u NTP1 , NTP2 —> using colon, or semicolon
service ntpd start